SdkLayout 5: Generalized matrix-vector multiplication (GEMV)
Contents
SdkLayout 5: Generalized matrix-vector multiplication (GEMV)¶
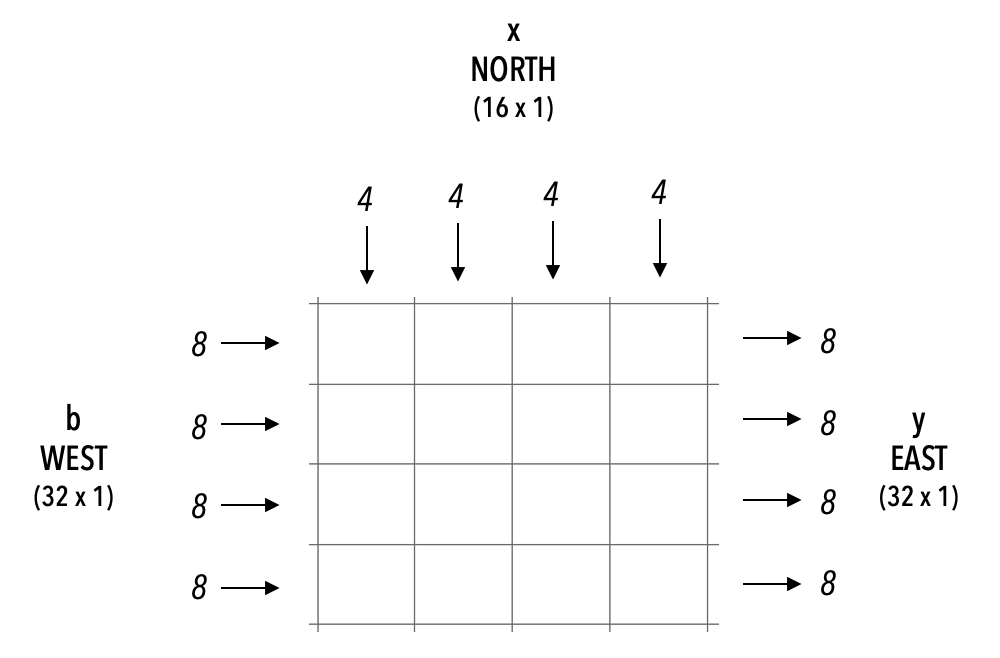
This tutorial demonstrates how we can put all the pieces together to write a GEMV program. Specifically, this tutorial implements the following GEMV formulation using 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point numbers:
y = Ax + b
Ais a tensor of shape [M, N] (stored distributed on PE memory).xis a tensor input of shape [N, 1] (streamed in).bis a tensor input of shape [M, 1] (streamed in).yis the tensor output of shape [M, 1] (streamed out).
For simplicity, we choose M as a multiple of the height of the kernel and N as a multiple of the width of the kernel. In this example, M = 32, N = 16 and we use a PE-rectangle (kernel) of size 4×4.
Below is a visualization of the kernel interface:
Note that this algorithm and the implementation are not optimized for performance. It is intended to serve as a non-trivial introductory example.
All computations are done in IEEE 754 FP32 format.
The matrix A, of shape [M, N],
is distributed across the PE memories as follows:
The first dimension of
A, M rows, is distributed across the height of the kernel.The second dimension of
A, N columns, is distributed across the width of the kernel.
Since we know that M is 32 and the height of the kernel is 4, each PE will be
assigned 32÷4 = 8 rows of A.
Similarly, each PE will get 16÷4 = 4 columns of A. This means each PE is
assigned an 8×4 chunk of the original matrix A.
This tutorial demonstrates a few more SDK+Paint features that are not covered by other previous tutorials. Most importantly, it shows how we can stream data to/from the host using I/O ports that consist of more than a single PE unlike the previous tutorial (see SdkLayout 4: Host-to-device and device-to-host data streaming) where I/O ports had only 1 PE.
As it is explained in the code comments, in order to achieve this we introduce a demux layer that demultiplex a single-PE input stream into the multi-PE input ports for vector ‘x’ and ‘b’. We also introduce a multiplexing layer that fuses a multi-PE stream back into a single-PE output stream for the result vector ‘y’.
gemv.csl¶
param x_in: color;
param b_in: color;
param y_out: color;
param width: u16;
param height: u16;
param control_ep: u16;
const x_in_q = @get_input_queue(0);
const b_in_q = @get_input_queue(1);
const y_out_q = @get_output_queue(0);
export var Ax_temp = @zeros([height]f32);
const dsd_Ax_temp = @get_dsd(mem1d_dsd, .{.tensor_access = |i|{height}->Ax_temp[i]});
export var A = @zeros([height, width]f32);
const dsd_A = @get_dsd(mem1d_dsd, .{.tensor_access = |i|{height}->A[i, 0], .wavelet_index_offset = true});
const in = @get_dsd(fabin_dsd, .{.extent = height, .fabric_color = b_in, .input_queue = b_in_q});
const out = @get_dsd(fabout_dsd, .{.extent = height, .fabric_color = y_out, .output_queue = y_out_q});
export var idx: u16 = 0;
// Wavelet-triggered task (WTT) that consumes the stream of vector 'x'.
const wtt_x_id = if (@is_arch("wse3")) @get_data_task_id(x_in_q) else @get_data_task_id(x_in);
task wtt_x(data: f32) void {
@fmacs(dsd_Ax_temp, dsd_Ax_temp, dsd_A, data, .{.index = 2 * idx});
idx += 1;
}
// This 'sentinel' task is a control-triggered task, i.e., a task
// that is activated by a control wavelet containing 'sentinel_id'
// in its payload.
// The demux layer is the one that will emit these control wavelets.
// Specifically, each PE in demux will emit a control wavelet to
// activate 'sentinel' once its done forwarding 'batch_size' elements
// of vector 'x'.
const sentinel_id = @get_control_task_id(control_ep);
task sentinel() void {
@fadds(out, in, dsd_Ax_temp, .{.async = true});
}
comptime {
@bind_data_task(wtt_x, wtt_x_id);
@bind_control_task(sentinel, sentinel_id);
@initialize_queue(x_in_q, .{.color = x_in});
@initialize_queue(b_in_q, .{.color = b_in});
if (@is_arch("wse3")) {
@initialize_queue(y_out_q, .{.color = y_out});
}
}
gemv.py¶
from cerebras.geometry.geometry import IntRectangle, IntVector
from cerebras.sdk.runtime.sdkruntimepybind import (
Color,
Edge,
Route,
RoutingPosition,
get_edge_routing,
)
def get_gemv(layout, name, width, height, batch_width, batch_height, control_ep, A):
gemv = layout.create_code_region('./gemv.csl', name, width, height)
###########
### Colors
###########
x_in = Color('x_in')
b_in = Color('b_in')
y_out = Color('y_out')
################
### Parameters
################
gemv.set_param_all('width', batch_width)
gemv.set_param_all('height', batch_height)
gemv.set_param_all('control_ep', control_ep)
gemv.set_param_all(x_in)
###########################
### Routing for vector 'x'
###########################
# The bottom row's routing is slightly different because we no longer
# need to forward data any further to the south. If we attempt to do that
# backpressure will stall the execution as there is no one to consume the
# stream on the south of the bottom row.
x_routes_core = (
RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.NORTH]).set_output([Route.RAMP, Route.SOUTH])
)
x_routes_bottom = (
RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.NORTH]).set_output([Route.RAMP])
)
x_bottom_routes = get_edge_routing(Edge.BOTTOM, [x_routes_bottom])
gemv.paint_all(x_in, [x_routes_core], [x_bottom_routes])
#######################
### Input port for 'x'
#######################
x_size = batch_width * width
x_port_routes = RoutingPosition().set_output([Route.RAMP, Route.SOUTH])
x_port = gemv.create_input_port(x_in, Edge.TOP, [x_port_routes], x_size)
#######################
### Input port for 'b'
#######################
b_size = batch_height * height
b_rx_routes = RoutingPosition().set_output([Route.RAMP])
b_port = gemv.create_input_port(b_in, Edge.LEFT, [b_rx_routes], b_size)
###############################
### Checkerboard pattern setup
###############################
# As the vector 'b' flows horizontally through the gemv code region
# it gets received by each PE, combined with the 'x' reduction for
# that tile, and it is then forwarded to the neighbouring PEs to the
# EAST using a different color. This means that initially at the left-most
# column color 'b_in' and color 'y_out' have their allocated values. However,
# in the next column, their values are swapped. That is, color 'b_in'
# has the value of color 'y_out' and vice versa.
receive_routes = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.WEST]).set_output([Route.RAMP])
sender_routes = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.RAMP]).set_output([Route.EAST])
# Since we have already specified the input port for 'b' above,
# we also setup routing for the partial result 'y' along the left-most
# column (i.e., the column that represents the input port for 'b').
ul = IntVector(0, 0)
lr = IntVector(1, height)
hot_pes = IntRectangle(ul, lr)
gemv.paint_range(hot_pes, y_out, [sender_routes])
gemv.set_param_range(hot_pes, b_in)
gemv.set_param_range(hot_pes, y_out)
# We now alternate the routing and code parameters between colors
# 'b_in' and 'y_out' to create the checkerboard pattern described above.
for i in range(1, width):
b_in, y_out = y_out, b_in
ul = IntVector(i, 0)
lr = IntVector(i + 1, height)
hot_pes = IntRectangle(ul, lr)
gemv.paint_range(hot_pes, b_in, [receive_routes])
gemv.paint_range(hot_pes, y_out, [sender_routes])
gemv.set_param_range(hot_pes, 'b_in', b_in)
gemv.set_param_range(hot_pes, 'y_out', y_out)
######################################
### Output port for result vector 'y'
######################################
y_tx_routes = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.RAMP])
y_port = gemv.create_output_port(y_out, Edge.RIGHT, [y_tx_routes], b_size, '_out')
#########################
### Set the value of 'A'
#########################
# Finally, we set the value of 2D matrix 'A' across the code region's PEs.
gemv.set_symbol_all('A', A, x_size, b_size)
return (x_port, b_port, y_port, gemv)
mux.csl¶
param size: u16;
param in_color: color;
param out_color: color;
const ctrl = @import_module("<control>");
const input_q = @get_input_queue(0);
const output_q = @get_output_queue(1);
const inDSD = @get_dsd(fabin_dsd, .{.extent = size,
.fabric_color = in_color,
.input_queue = input_q});
const outDSD = @get_dsd(fabout_dsd, .{.extent = size,
.fabric_color = out_color,
.output_queue = output_q});
const ctrlOurDSD = @get_dsd(fabout_dsd, .{.extent = 1,
.fabric_color = out_color,
.output_queue = output_q,
.control = true});
const main_id = @get_local_task_id(8);
task main() void {
@mov32(outDSD, inDSD, .{.async = true, .activate = send_ctrl});
}
// This task sends a control wavelet to self, in order to
// advance the switch position.
const send_ctrl_id = @get_local_task_id(9);
task send_ctrl() void {
@mov32(ctrlOurDSD, ctrl.encode_single_payload(ctrl.opcode.SWITCH_ADV, true, {}, 0));
}
comptime {
@bind_local_task(main, main_id);
@activate(main_id);
@bind_local_task(send_ctrl, send_ctrl_id);
@initialize_queue(input_q, .{.color = in_color});
if (@is_arch("wse3")) {
@initialize_queue(output_q, .{.color = out_color});
}
}
mux.py¶
from cerebras.sdk.runtime.sdkruntimepybind import (
Edge,
Route,
RoutingPosition,
)
# The mux code region does the inverse job of the demux code region.
# Specifically, it multiplexes the output wavelets from the gemv's
# multi-PE output port for result vector 'y', into a single-PE
# stream that can then be connected to an output stream towards the
# host.
#
# Each PE in the mux layer (which is positioned vertically in this
# example but it can have any orientation) receives 'batch_size'
# wavelets. However, only the PE associated with the single-PE output
# port at the top is able to forward its wavelets out and towards the
# host.
#
# Once 'batch_size' wavelets are forwarded though, a control wavelet
# is emitted to switch the routing position such that the incoming flow
# of wavelets is now received from the south (i.e., from the rest of
# the PEs in the mux layer) and then forwarded out of the single-PE
# output port towards the host.
#
# With that mechanism, one-by-one each PE forwards its 'batch_size'
# wavelets upwards and towards the output port and eventually to the
# host.
#
# stream 1st batch stream 2nd batch
# to the host to the host
# ^ ^
# | |
# +---|----+ +---|----+
# | | | | | |
# host data--------->o | host data | o |
# (batch_size) | | (batch_size) | ^ |
# |---^----| |---|----|
# | | | | | |
# host data--------->o | host data--------->o |
# (batch_size) | | (batch_size) | |
# |--------| |--------|
# | | | |
# | . | | . |
# | . | | . |
# | . | | . |
# | | | |
# +--------+ +--------+
#
def get_mux(layout, name, batch_size, width, height):
mux = layout.create_code_region('./mux.csl', name, width, height)
mux.set_param_all('size', batch_size)
in_color = mux.color('in_color')
out_color = mux.color('out_color')
mux.set_param_all(in_color)
mux.set_param_all(out_color)
core_out_route = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.RAMP]).set_output([Route.NORTH])
forward_route = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.SOUTH]).set_output([Route.NORTH])
mux.paint_all(out_color, [core_out_route, forward_route])
input_routes = RoutingPosition().set_output([Route.RAMP])
output_routes = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.RAMP])
forward_port_routes = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.SOUTH])
size = batch_size * height
in_port = mux.create_input_port(in_color, Edge.LEFT, [input_routes], size)
out_port = mux.create_output_port(
out_color, Edge.TOP, [output_routes, forward_port_routes], size
)
return (in_port, out_port, mux)
demux.csl¶
param size: u16;
param in_color: color;
param out_color: color;
param entry_point: u16;
param has_sentinel: u16;
const ctrl = @import_module("<control>");
const input_q = @get_input_queue(0);
const output_q = @get_output_queue(0);
const inDSD = @get_dsd(fabin_dsd, .{.extent = size,
.fabric_color = in_color,
.input_queue = input_q});
const outDSD = @get_dsd(fabout_dsd, .{.extent = size,
.fabric_color = out_color,
.output_queue = output_q});
const ctrlOurDSD = @get_dsd(fabout_dsd, .{.extent = 1,
.fabric_color = out_color,
.output_queue = output_q,
.control = true});
const main_id = @get_local_task_id(8);
task main() void {
@mov32(outDSD, inDSD, .{.async = true, .activate = send_sentinel});
}
// This task will optionally send a control wavelet.
// This is needed by the 'x' vector to signal the gemv PEs
// that the partial A*x result has been computed and the
// 'b' vector can now be added to it.
const ctrl_entry_pt = @get_control_task_id(entry_point);
const send_sentinel_id = @get_local_task_id(9);
task send_sentinel() void {
if (has_sentinel > 0) {
@mov32(ctrlOurDSD, ctrl.encode_control_task_payload(ctrl_entry_pt));
}
}
comptime {
@bind_local_task(main, main_id);
@bind_local_task(send_sentinel, send_sentinel_id);
@activate(main_id);
@initialize_queue(input_q, .{.color = in_color});
if (@is_arch("wse3")) {
@initialize_queue(output_q, .{.color = out_color});
}
}
demux_adaptor.csl¶
param batch_size: u16;
param num_batches: u16;
param in_color: color;
param out_color: color;
// Local task IDs.
const local_ids = .{8, 9};
const ctrl = @import_module("<control>");
const input_q = @get_input_queue(0);
const output_q = @get_output_queue(0);
const inDSD = @get_dsd(fabin_dsd, .{.extent = batch_size,
.fabric_color = in_color,
.input_queue = input_q});
const outDSD = @get_dsd(fabout_dsd, .{.extent = batch_size,
.fabric_color = out_color,
.output_queue = output_q});
const ctrlOurDSD = @get_dsd(fabout_dsd, .{.extent = 1,
.fabric_color = out_color,
.output_queue = output_q,
.control = true});
// Control wavelet buffer and corresponding memory DSD.
const ctrl_buffer = [1]u32{ctrl.encode_single_payload(ctrl.opcode.SWITCH_ADV, true, {}, 0)};
const ctrl_dsd = @get_dsd(mem1d_dsd, .{.base_address = &ctrl_buffer, .extent = 1});
var i: u16 = 0;
const main_id = @get_local_task_id(local_ids[0]);
task main() void {
// When we process the last batch, we don't need to send a
// control wavelet. That's because the last PE of the demux
// layer doesn't need to advance its switch position.
if (i == num_batches - 1) {
@mov32(outDSD, inDSD, .{.async = true});
return;
}
@mov32(outDSD, inDSD, .{.async = true, .activate = send_ctrl});
i += 1;
}
// Control wavelet is sent here to trigger the advancement of
// the switch position of the next demux PE.
const send_ctrl_id = @get_local_task_id(local_ids[1]);
task send_ctrl() void {
@mov32(ctrlOurDSD, ctrl_dsd, .{.async = true, .activate = main});
}
comptime {
@bind_local_task(main, main_id);
@activate(main_id);
@bind_local_task(send_ctrl, send_ctrl_id);
@initialize_queue(input_q, .{.color = in_color});
if (@is_arch("wse3")) {
@initialize_queue(output_q, .{.color = out_color});
}
}
demux.py¶
from cerebras.sdk.runtime.sdkruntimepybind import (
Edge,
Route,
RoutingPosition,
get_edge_routing,
)
# The demux adaptor is a single-PE code region that is responsible for controlling
# the behavior of the demux layer (see below).
#
# Specifically, the demux adaptor forwards all the data from the host
# to the demux layer while injecting control signals after every 'batch_size'
# number of wavelets. These control signals help the demux layer distribute the
# data evenly across a 1D vector of PEs such that each PE in the demux layer
# forwards 'batch_size' wavelets to the user's port.
#
# Demux
# adaptor Demux
# +-------+ +--------------------------------------+
# | | | | | |
# host data----->| |----->|-->o |-->o | ... |
# | | | | | | | |
# +-------+ +---|---+---|---+----------------------+
# | |
# V V
# batch
# size
#
# Demux
# adaptor Demux
# +-------+ +--------------------------------------+
# | | ctrl | | | |
# host data----->| |----->|-->o---|-->o | ... |
# | | | | | | |
# +-------+ +-------+---|---+----------------------+
# |
# V
# batch
# size
def get_demux_adaptor(layout, name, batch_size, num_batches):
demux_adaptor = layout.create_code_region('./demux_adaptor.csl', name, 1, 1)
demux_adaptor.set_param_all('batch_size', batch_size)
demux_adaptor.set_param_all('num_batches', num_batches)
in_color = demux_adaptor.color('in_color')
out_color = demux_adaptor.color('out_color')
demux_adaptor.set_param_all(in_color)
demux_adaptor.set_param_all(out_color)
input_routes = RoutingPosition().set_output([Route.RAMP])
output_routes = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.RAMP])
size = batch_size * num_batches
in_port = demux_adaptor.create_input_port(in_color, Edge.LEFT, [input_routes], size)
out_port = demux_adaptor.create_output_port(
out_color, Edge.RIGHT, [output_routes], size
)
return (in_port, out_port, demux_adaptor)
# The goal of the demux layer is to connect an input stream from the host
# to a port that spans more than a single PE. That's because I/O streams
# to/from the host go through a single PE device port (in the future, this
# restriction can be lifted). This means that if a user wants to stream
# data from the host to a multi-PE port (which is the case for the 'x'
# and 'b' vectors in this gemv tutorial) then data need to be demultiplexed
# from a single-PE stream to a multi-PE stream.
#
# The demux layer achieves that in combination with the previous demux
# adaptor layer, by forwarding the first 'batch_size' number of wavelets
# from the first PE, the next 'batch_size' number of wavelets from the
# second PE and so on (see diagram above).
#
# This is achieved by utilizing the switching capability of the WSE where
# a control wavelet sent by the demux adaptor, instructs the PE router
# to move to a new routing position (see diagram above).
#
# The x demux layer differs from the b demux layer in that it is positioned
# horizontally. There is no need to do that but it helps to demonstrate a
# variation of the layer with different routing charachteristics.
#
# In addition, the x demux layer will also enable a control entry point
# after 'batch_size' wavelets are sent. This entry point informs the
# gemv kernel that the reduction of the x vector is done for a given tile
# which means that the b vector can now be added to the result.
def get_x_demux(layout, name, batch_size, width, height, entry_point):
demux = layout.create_code_region('./demux.csl', name, width, height)
demux.set_param_all('size', batch_size)
demux.set_param_all('has_sentinel', 1)
demux.set_param_all('entry_point', entry_point)
in_color = demux.color('in_color')
out_color = demux.color('out_color')
demux.set_param_all(in_color)
demux.set_param_all(out_color)
# All PEs begin at pos1. This means that only the left-most PE
# (i.e., the PE associated with the demux layer's input port) is able
# to forward data to the gemv kernel at the beginning.
# Once a control wavelet lands, each PE that receives it moves to pos2
# which will effectively forward all remaining wavelets to the rest
# of the PEs in the demux layer.
#
# Finally, the right-most PE doesn't need pos2 because it forwards
# the last batch of data (i.e., no more data need to be forwarded).
pos1 = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.WEST]).set_output([Route.RAMP])
pos2 = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.WEST]).set_output([Route.EAST])
edge_route = get_edge_routing(Edge.RIGHT, [pos1])
demux.paint_all(in_color, [pos1, pos2], [edge_route])
input_routes = RoutingPosition().set_output([Route.RAMP])
output_routes = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.RAMP])
size = batch_size * width * height
blah = RoutingPosition().set_output([Route.EAST])
in_port = demux.create_input_port(in_color, Edge.LEFT, [input_routes, blah], size)
out_port = demux.create_output_port(out_color, Edge.BOTTOM, [output_routes], size)
return (in_port, out_port, demux)
# Same as the x demux layer but with two key differences:
#
# - It is positioned vertically and therefore routing is different.
# In the future, the SdkLayout API will support a 'flip' operation
# on code regions which will allow us to re-use the x demux layer
# by simply flipping it.
#
# - The b demux layer does not need to send a control signal to the
# gemv code regions because no more action is needed once the 'b'
# vector is done being streamed through the gemv code region.
def get_b_demux(layout, name, batch_size, width, height):
demux = layout.create_code_region('./demux.csl', name, width, height)
demux.set_param_all('size', batch_size)
demux.set_param_all('has_sentinel', 0)
demux.set_param_all('entry_point', 0)
in_color = demux.color('in_color')
out_color = demux.color('out_color')
demux.set_param_all(in_color)
demux.set_param_all(out_color)
core_out_route = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.NORTH]).set_output([Route.RAMP])
forward_route = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.NORTH]).set_output([Route.SOUTH])
edge_route = get_edge_routing(Edge.BOTTOM, [core_out_route])
demux.paint_all(in_color, [core_out_route, forward_route], [edge_route])
input_routes = RoutingPosition().set_output([Route.RAMP])
output_routes = RoutingPosition().set_input([Route.RAMP])
size = batch_size * width * height
blah = RoutingPosition().set_output([Route.SOUTH])
in_port = demux.create_input_port(in_color, Edge.TOP, [input_routes, blah], size)
out_port = demux.create_output_port(out_color, Edge.RIGHT, [output_routes], size)
return (in_port, out_port, demux)
run.py¶
#!/usr/bin/env cs_python
import argparse
import numpy as np
from cerebras.sdk.runtime.sdkruntimepybind import (
SdkLayout,
SdkTarget,
SdkRuntime,
SimfabConfig,
get_platform,
)
from demux import get_demux_adaptor, get_x_demux, get_b_demux
from mux import get_mux
from gemv import get_gemv
def get_random_data(size):
return np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0, size).astype(np.float32)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--cmaddr', help='IP:port for CS system')
parser.add_argument(
'--arch',
choices=['wse2', 'wse3'],
default='wse3',
help='Target WSE architecture (default: wse3)'
)
args = parser.parse_args()
###########
### Layout
###########
# If 'cmaddr' is empty then we create a default simulation layout.
# If 'cmaddr' is not empty then 'config' and 'target' are ignored.
config = SimfabConfig(dump_core=True)
target = SdkTarget.WSE3 if (args.arch == 'wse3') else SdkTarget.WSE2
platform = get_platform(args.cmaddr, config, target)
layout = SdkLayout(platform)
######################
### Common invariants
######################
data_width = 16
data_height = 32
pe_width = 4
pe_height = 4
batch_width = data_width // pe_width
batch_height = data_height // pe_height
control_ep = 40
#########
### Data
#########
x = get_random_data(data_width)
b = get_random_data(data_height)
A = get_random_data(data_width * data_height)
y = np.empty(data_height, dtype=np.float32)
#############
### Vector X
#############
(x_port, x_adaptor_port, x_adaptor) = get_demux_adaptor(
layout, 'x_demux_adaptor', batch_width, pe_width
)
x_adaptor.place(1, 0)
(x_demux_port, x_out_port, x_demux) = get_x_demux(
layout, 'x_demux', batch_width, pe_width, 1, control_ep
)
x_demux.place(5, 0)
layout.connect(x_adaptor_port, x_demux_port)
#############
### Vector b
#############
(b_port, b_adaptor_port, b_adaptor) = get_demux_adaptor(
layout, 'b_demux_adaptor', batch_height, pe_height
)
b_adaptor.place(1, 2)
(b_demux_port, b_out_port, b_demux) = get_b_demux(
layout, 'b_demux', batch_height, 1, pe_height
)
b_demux.place(3, 2)
layout.connect(b_adaptor_port, b_demux_port)
#########
### GEMV
#########
(gemv_x_port, gemv_b_port, gemv_y_port, gemv) = get_gemv(
layout, 'gemv', pe_width, pe_height, batch_width, batch_height, control_ep, A
)
gemv.place(5, 2)
#############
### Vector y
#############
(y_in_port, y_port, y_mux) = get_mux(layout, 'y_mux', batch_height, 1, pe_height)
y_mux.place(10, 2)
#####################
### Port connections
#####################
layout.connect(x_out_port, gemv_x_port)
layout.connect(b_out_port, gemv_b_port)
layout.connect(gemv_y_port, y_in_port)
################
### I/O streams
################
x_stream = layout.create_input_stream(x_port)
b_stream = layout.create_input_stream(b_port)
y_stream = layout.create_output_stream(y_port)
################
### Compilation
################
compile_artifacts = layout.compile(out_prefix='out')
##############
### Execution
##############
runtime = SdkRuntime(compile_artifacts, platform, memcpy_required=False)
runtime.load()
runtime.run()
##################################
### Send 'x' and 'b'. Receive 'y'
##################################
# Vectors 'x' and 'b' must be sent asynchronously (i.e., in a
# non-blocking fashion) to prevent a deadlock due to their
# inter-dependence in the core gemv computation kernel.
runtime.send(x_stream, x, nonblock=True)
runtime.send(b_stream, b, nonblock=True)
runtime.receive(y_stream, y, data_height, nonblock=True)
runtime.stop()
#################
### Verification
#################
A_matrix = A.reshape(data_height, data_width)
expected = np.dot(A_matrix, x) + b
assert np.allclose(expected, y, atol=1e-6)
print("SUCCESS!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
commands.sh¶
#!/usr/bin/env bash
set -e
cs_python run.py --arch=wse3